D Value Z Value
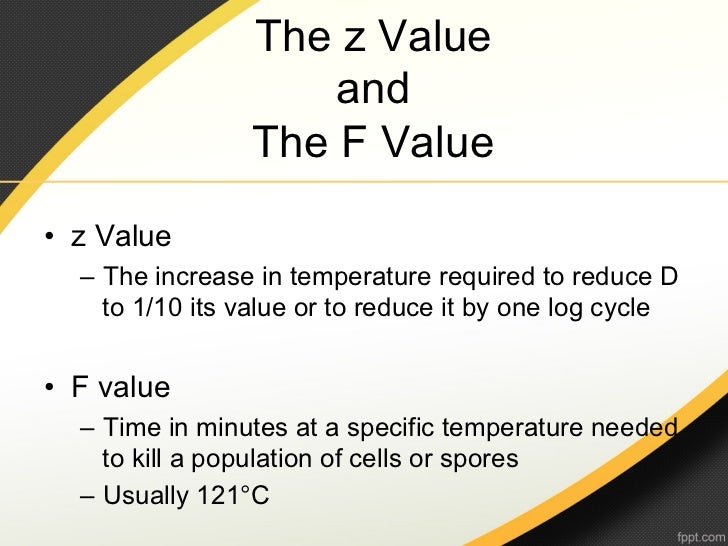
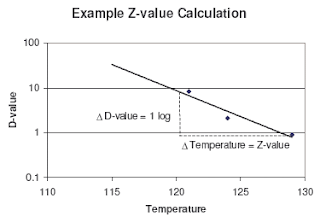
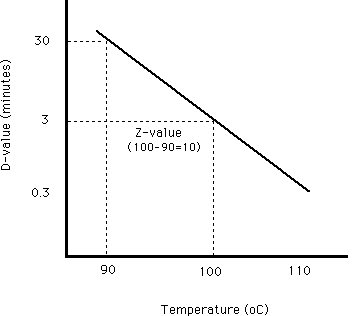
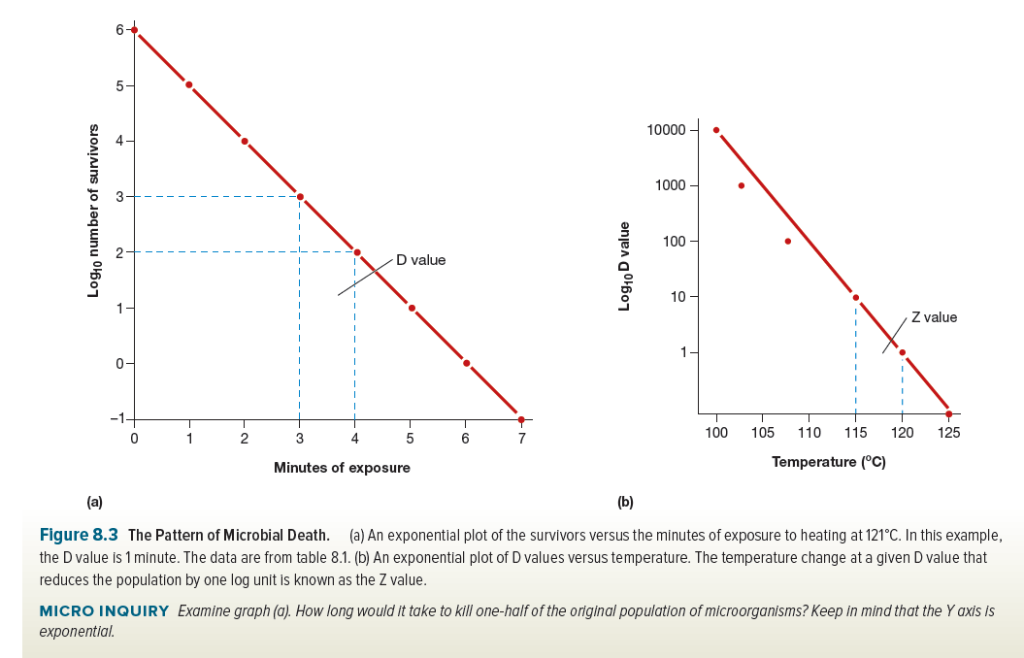
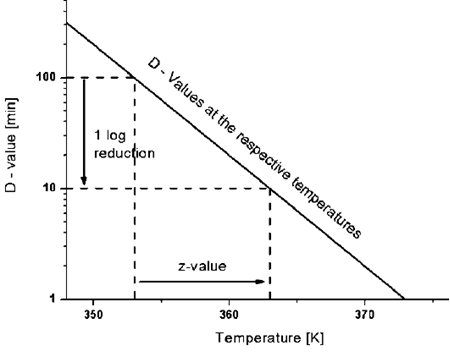
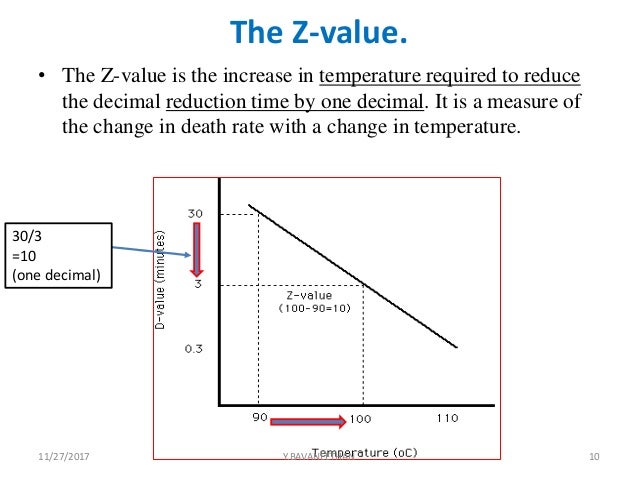
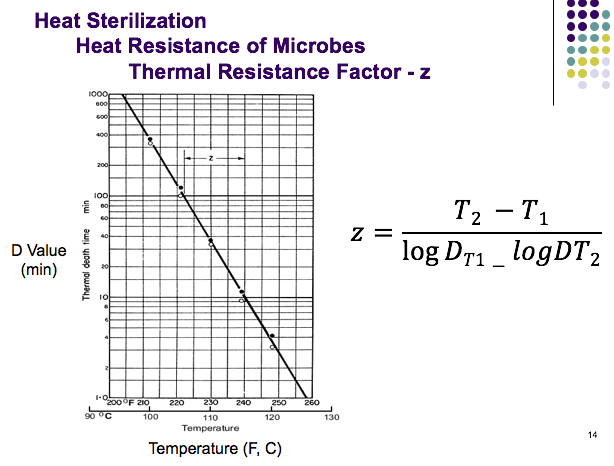
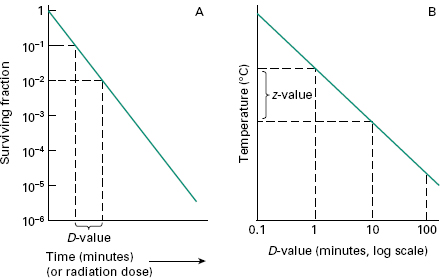
Z value z value is the number of degrees of temperature change necessary to change the d value by a factor of 10.
D value z value. 2 z 18 f and indicates that if a process is raised 18 f. Significant differences were found for the d and z values among the five products. In the illustration below the z value is 10 c. However it now has analogous uses in other microbial resistance and death rate applications such as for ethylene oxide and.
It is defined as the temperature change required to change the d value by a factor of 10. The table below is a right tail z table. Thus after an exposure time of 1 d only 10 of the organisms originally present in a microbial colony would remain. The z value is a measure of the change of the d value with varying temperature and is a simplified version of an arrhenius equation and it is equivalent to z 2 303 rt t ref e.
A d value is denoted with the capital letter d. The z value reflects the temperature dependence of the reaction. At 55 to 70 degrees c. The key difference between d value and z value is that d value is the time required to kill 90 of microorganisms at a specific temperature while z value measures the number of degrees the temperature should be increased to achieve a tenfold reduction in d value.
As shown in fig. Thermal death time refers to the time taken for a specific bacterium to kill at a specific temperature. The z value for spore death time typically ranges between 16 to 20 f. It is used to find the area between z 0 and any positive value and reference the area to the right hand side of the standard deviation curve.
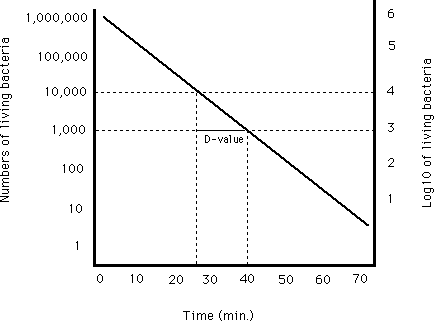
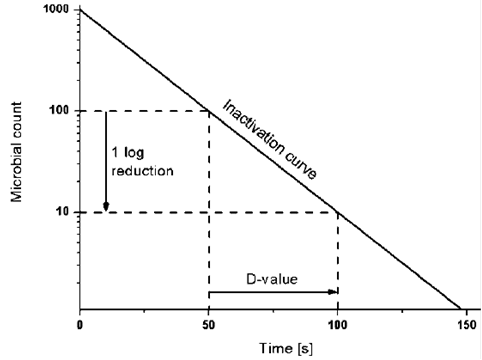
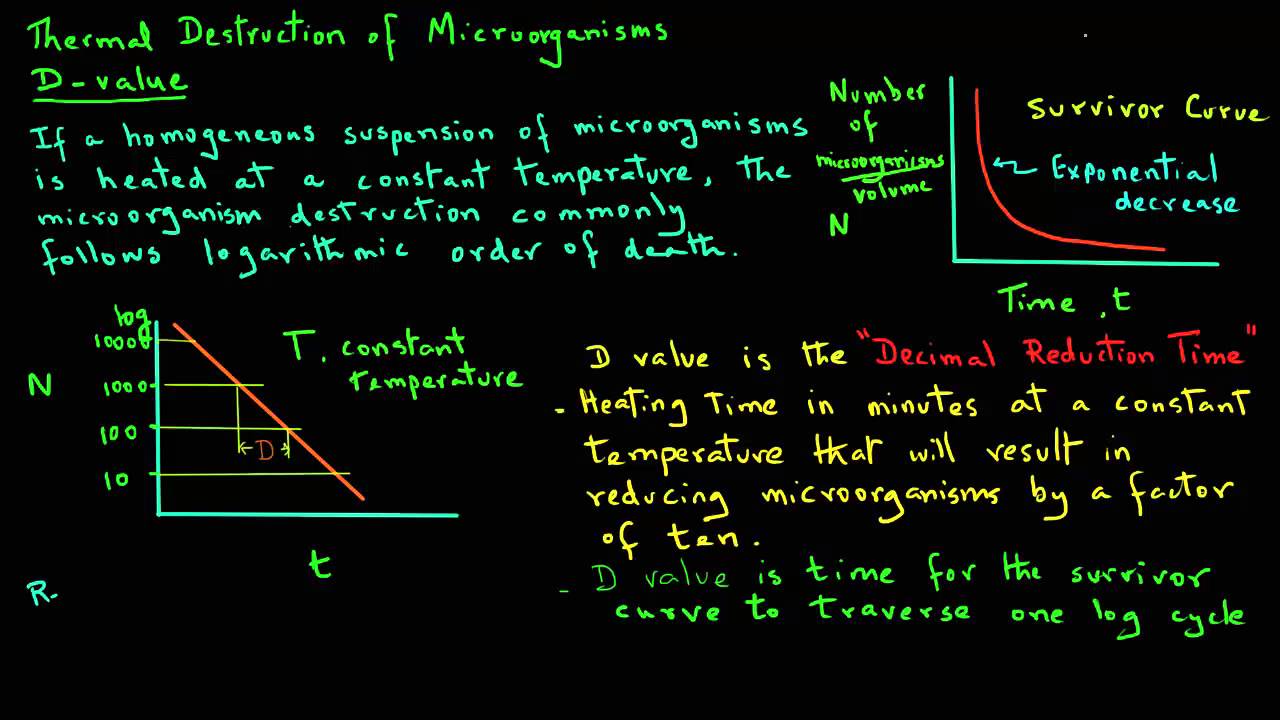
For the five tested products the d values for the salmonella serotypes and l. D value decimal reduction value it is the time required at temperature t to reduce a specific microbial population by 90 or by a factor of 10. The z value of an organism in a particular medium is the temperature change required for the d value to change by a factor of ten or put another way the temperature required for the thermal destruction curve to move. Reactions that have small z values are highly temperature dependent.
The term originated in assessments of microbes thermal resistance and in thermal death time analysis. Innocua were 26 97 to 0 25 min and 191 94 to 0 18 min respectively and their z values were 7 60 to 9 83 degrees c and 4 86 to 8 67 degrees c respectively. Calculator for determining the decimal reduction time d for a microorganism at a higher temperature knowing the d value at a lower temperature and the z value.