D Value Z Value F Value

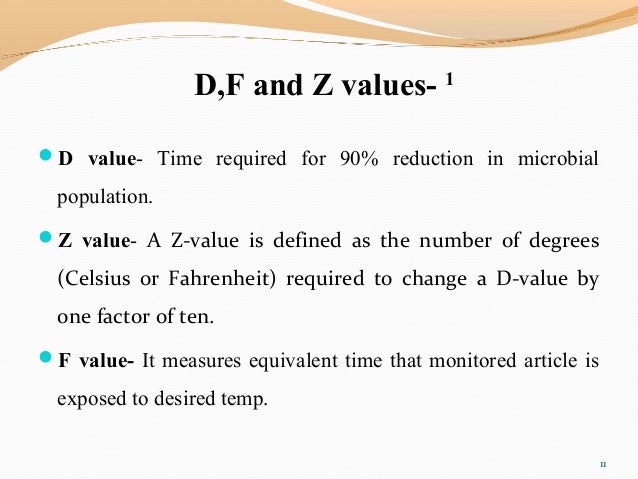
A description of d and f values as used in thermal processing of foods.
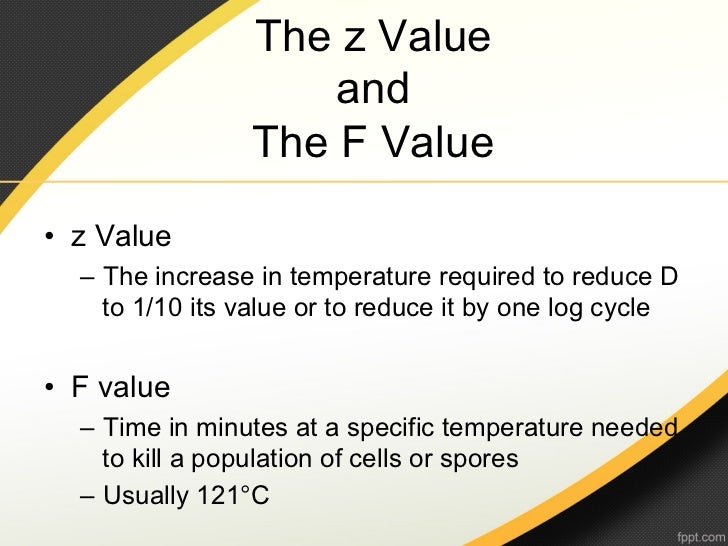
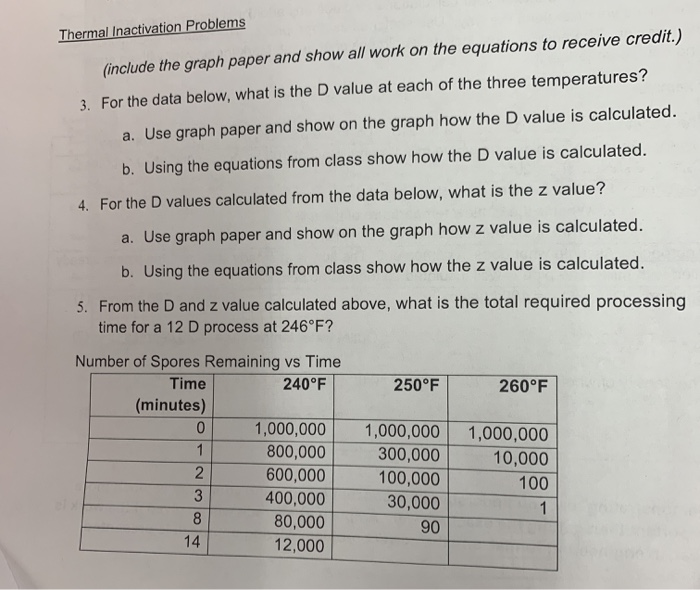
D value z value f value. In the practical sense it is a measure of how susceptible a spore population is to changes in temperature. Or f 240 12 min. To refer back to the original example where the d 240 was 1 min the f value for the process would be 12 min. It is the number of degrees the temperature has to be increased to achieve a tenfold i e.
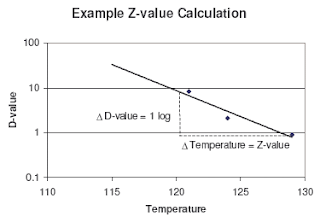
The values for f reported in the literature do not seem to be very consistent perkins 1956. So the z value allows us to calculate a thermal process of equivalency if we have one d value and the z value. So if it takes an increase of 10 to move the curve one log then our z value is 10. When f is used without a subscript indicating temperature 250 f is.
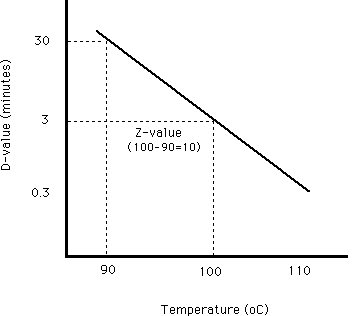
Z value is the number of degrees of temperature change necessary to change the d value by a factor of 10. A z value is defined as the number of degrees celsius or fahrenheit required to change a d value by one factor of ten. Using the values given by the mrc 121 c for 15 min and 134 c for 3 min one obtains d 2 5 min and z 18 6 c. Van asten et al.
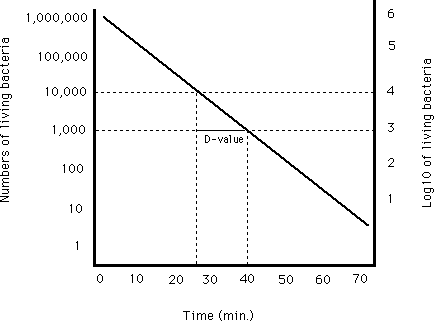
For example if d value at 121ºc is 1 5 min z value is 10ºc. The d value of an organism is the time required in a given medium at a given temperature for a ten. D z and f value in thermal processing. Then d value at 131ºc will be 0 15 minute.
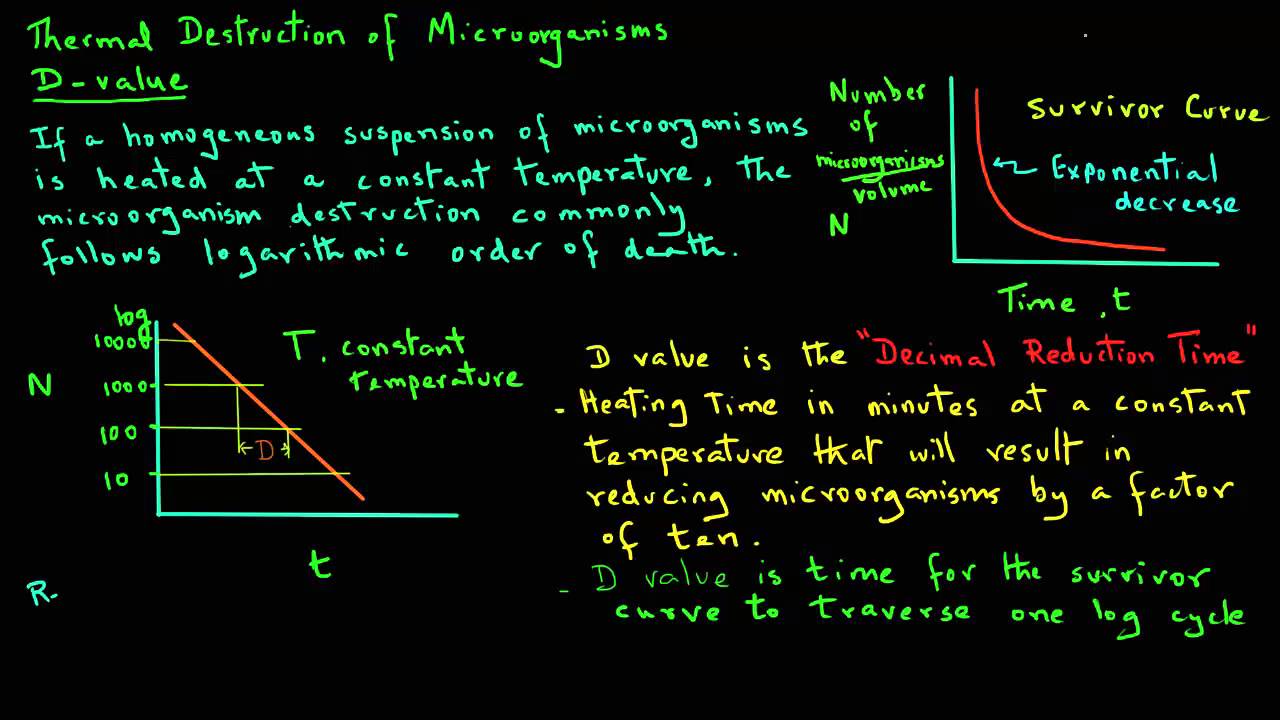
Z value is a term used in microbial thermal death time calculations. 1 log 10 reduction in the d value. So then if we have a d value of 4 5 minutes at 150 we can calculate d values for 160 by reducing the time by 1 log.