D Value In Food Preservation
The f value for a process is the number of minutes required to kill a known population of microorganisms in a given food under specified conditions.
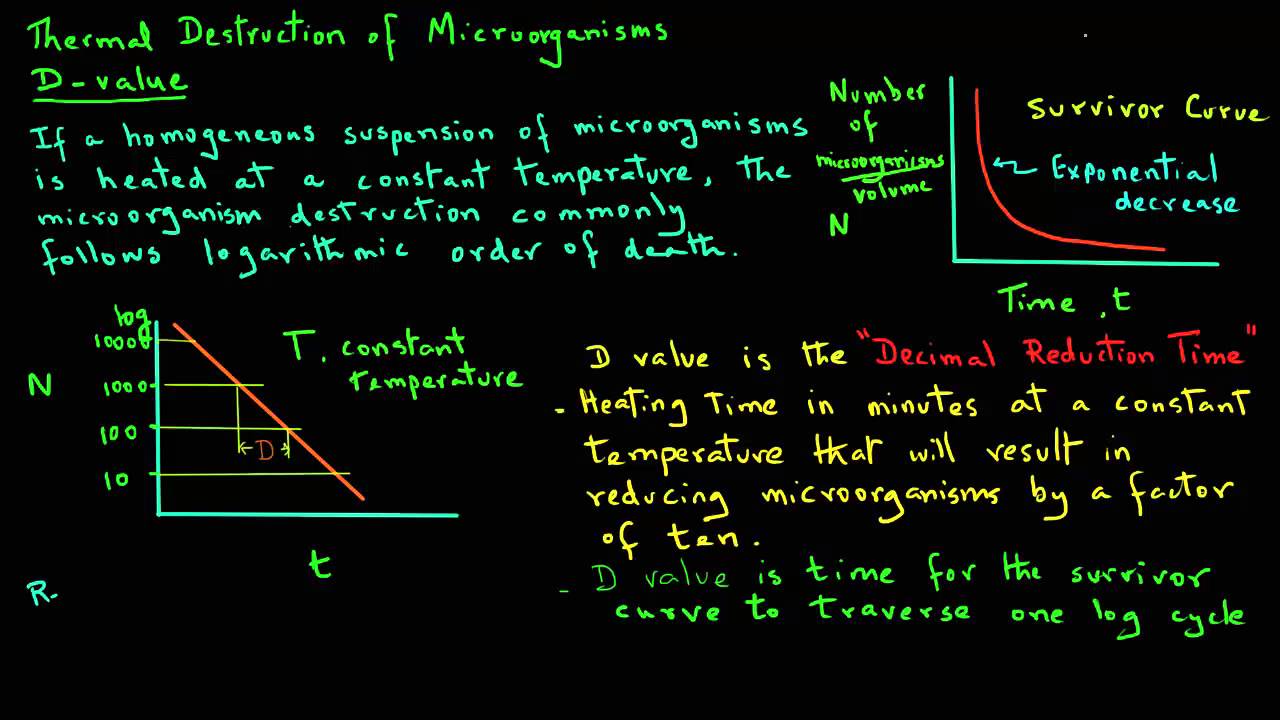
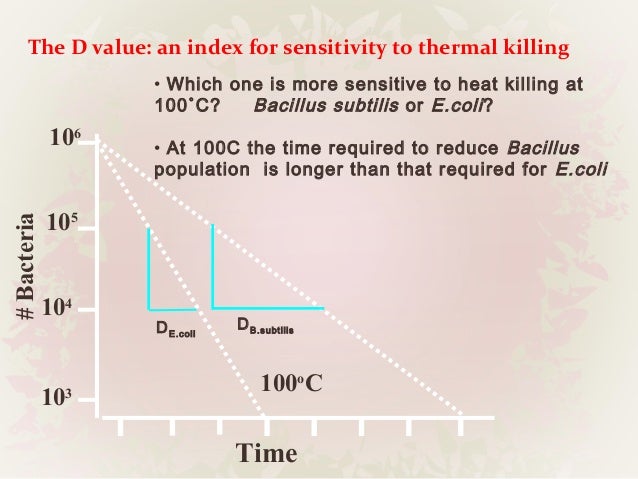
D value in food preservation. Hence d value is the measure of death rate of microorganisms. This f value is usually set at 12 d values. It reflects the resistance of an organism to a specific temperature and can be used to compare the relative heat resistance among different organisms spores. An ancient practice designed to prevent spoilage among the first food preservation practices were the salting of meat and fish adding sugar in canned foods and pickling vegetables.
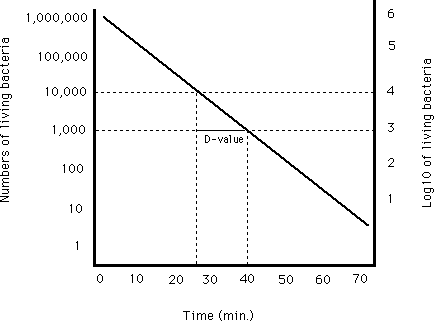
Botulinum spores by 12 logs or 12 d at 250 the temperature used in the calculation of most commercial 12 d processes is 250 and the d value for this organism at 250 is 0 21 minutes. In the illustration below the d value is 14 minutes 40 26 and would be representative of a process at 72 c. In 1875 the ammonia refrigeration system that was capable of. Today preservatives continue this important role.
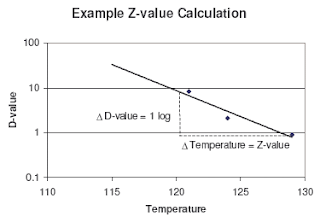
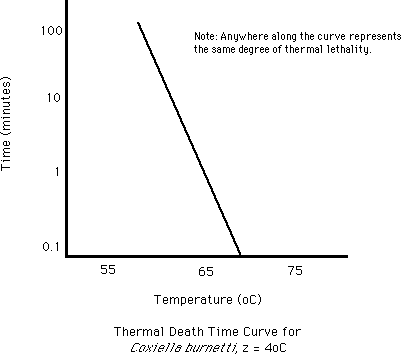
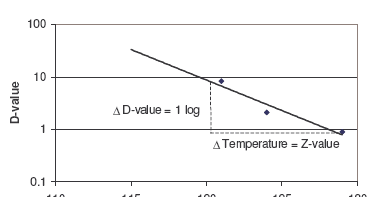
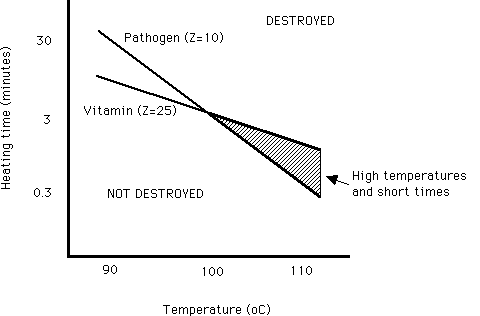
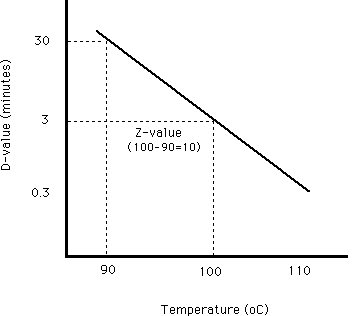
Thus the d value or decimal reduction time decreases the surviving population by one log cycle. Food preservatives play a vital role in preventing deterioration of food protecting against spoilage from mold yeast life threatening botulism and. The z value reflects the temperature dependence of the reaction. Determination of z value for biological indicators.
For example if d value at 121ºc is 1 5 min z value is 10ºc. Food preservation by cooling and freezing are the oldest methods using natural. D value for the same organism varies depending on the food type. For example a d value at 72 c of 1 minute means that for each minute of processing at 72 c the bacteria population of the target microorganism will be reduced by 90.
However in modern food production canned foods are subjected to a time temperature process that will reduce the probability of the survival by the most heat resistant c. D value is lower in acid foods and higher in presence of. The d value is real.